What is Obesity
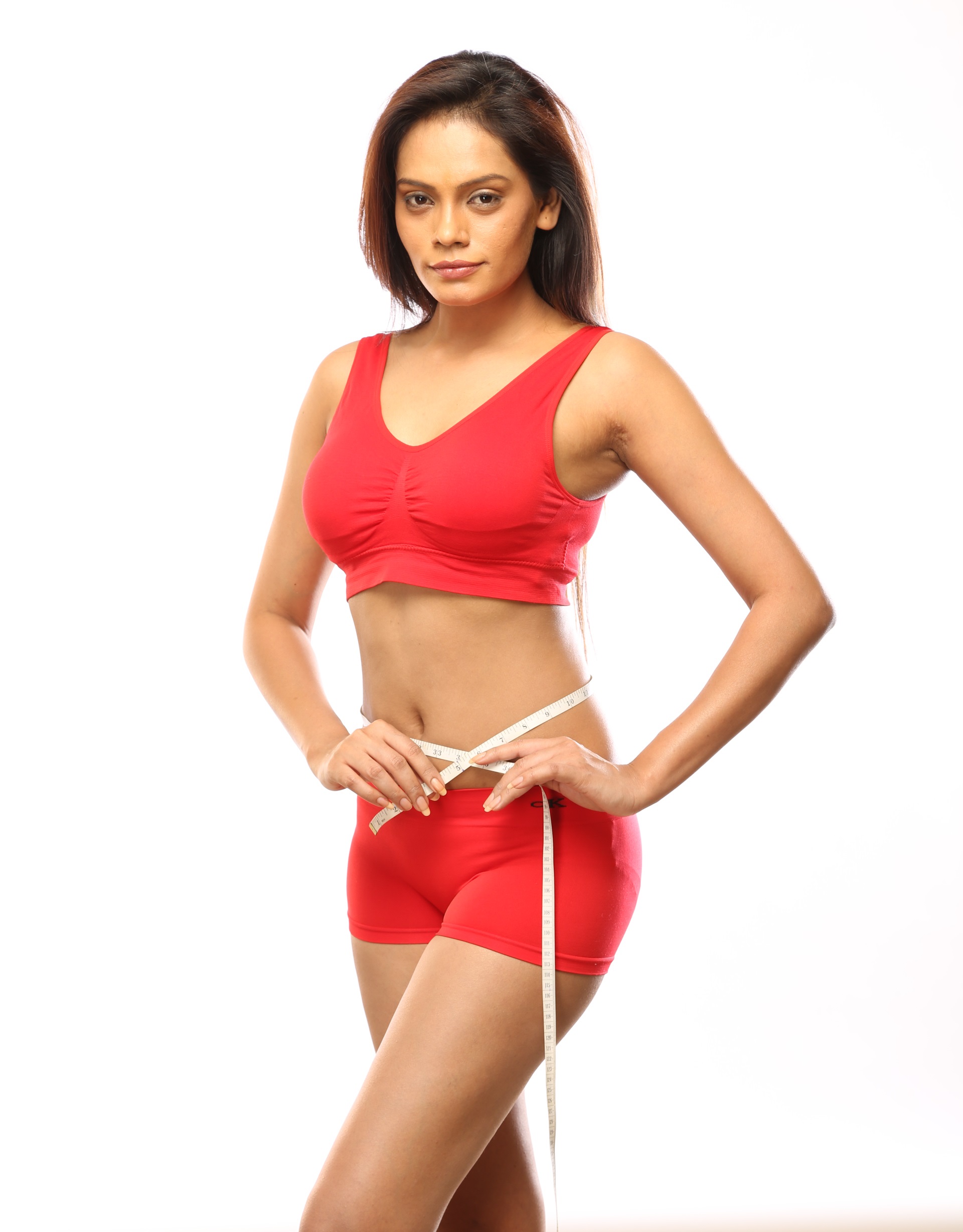
A certain amount of body fat is necessary for storing energy, heat insulation, shock absorption, and other functions. However, when the fat exceeds the amount that is necessary it leads to a condition called obesity.
In general, overweight and obesity indicates a weight which is greater than what is considered healthy. Obesity is a complex disorder in which excess body fat has accumulated excessively so that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to increased disease incidence and decreased life expectancy.
People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI) is over 30 kg/m2, with the range 25–30 kg/m2 defined as overweight. Obesity increases the likelihood of various diseases, particularly heart disease, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, and certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
Obesity is one of the most pervasive, chronic diseases in need of new strategies for medical treatment and care. As a leading cause of world’s mortality, morbidity, disability, healthcare utilization and healthcare costs. The high prevalence of obesity continues to strain the healthcare systems.
Basically, overweight is a result of too much intake of food or ah failure of the body to utilize the energy for daily body use. As a result, these extra energies are stored as fat and although there is no specific food that can really pinpoint where fat will be built up in the body, the uniqueness of each person dictates where or in what areas of the body these fats will be stored.